Service Management Policy
1. IT SERVICES MANAGEMENT POLICY
The Company has always expressed its interest in the formalization of processes, both at a technical and management level, since its creation and has progressively incorporated good practices in Service Management with the adoption of different aspects of the ITIL methodology.
The organization of the company as a set of services provides a vision of technology based on the needs of customers -both internal and external- and on quality and service level commitments.
This approach breaks with the usual practice of organizing IT services as hierarchically structured independent units. Therefore, its implementation can generate rejection in the organization and must be carefully planned to guarantee its success.
As a first measure for a correct implementation of IT Service Management in the Company, an IT Service Management policy has been defined, fundamentally based on the following points:
1. All activity carried out by the Company as a consequence of the delivery of projects to its Clients must be able to be included in the IT services defined in the scope.
2. The complete list of services must be kept up-to-date in a map of services that must be public and known by all members of the organization. It must also be available to the clients of the services that do not belong to the organization and to the suppliers that in one way or another participate in the provision of the services.
3. A Service Management system (hereinafter, SGS) is defined based on ITIL practices.
4. It is the vocation of The Company that the Services included in the Catalog be certified with the ISO 20000/27001/ENS standard as a measure to ratify its correct definition and implementation.
5. There is an “SGS05 Service Management Plan” where all the characteristics inherent to the SMS are defined. It is a public document and accessible by all members of the organization.
6. There is a document “SGS01 Roles and Responsibilities”, which defines the roles and responsibilities related to the performance of IT Service Management, from the General Management to those responsible for Process and Service.
2. OBJECTIVES OF SERVICE MANAGEMENT
The first objective of Service Management in The Company is to improve the satisfaction of service users. It is understood that with the adoption of ITIL practices and the certification of these under the ISO 20000/27001/ENS standard, the attention to users and the provision of services will improve significantly.
A second objective is to apply the experience and knowledge to the services that the company designs and offers to its clients. It is understood that if the company certifies the services it offers under a regularized service catalogue, it will be able to demonstrate its solvency in their technical implementation and, in general, reorient its relationship with the client based on well-defined, uniform services, and with guaranteed service quality commitments, guiding offers and solutions towards service provision.
These objectives are reflected in the Service Management Plan.
The benefits obtained with the implementation of the Service Management policy are the following:
1. Align IT services to business needs
2. Improve the provision of the service and attention to customers and users.
3. Provide an added value of trust, improving its image compared to other companies and becoming a decision factor against the competition.
4. Increase customer satisfaction for the services they receive from the company.
• Service Management Plan
There is a document called “SGS05 Service Management Plan” that is reviewed annually. It defines the scope, objectives, requirements, processes, etc. of the management of services within the scope of the ISO 20000/27001/ENS certification.
The Service Management Plan defines the following phases:
1. SMS Planning: Includes the allocation of budgets and funds, assignment of roles and responsibilities, process documentation, risk identification and management, work team management, equipment and budget management, progress information, and coordination of Service Management processes.
2. Monitoring and review: Includes analysis of indicators, system audits and system reviews) and continuous improvement.
3. CATALOG OF SERVICES
The services subject to the scope of the SGTI are defined in the document “SGS00 Service Catalogue”, and includes the following:
• Support to GIS projects
• Support for Java projects
• Support for MicroSoft projects
• OutTasking service
The following table summarizes the services under the scope of the SMS, indicating the processes that are included in the scope for each Service:
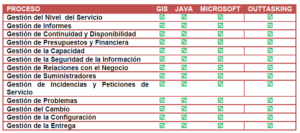
4. SCOPE
The scope of application of IT Service Management in its current definition applies to the services provided by the GIS, Java and Microsoft areas in their relationship with clients, from the first delivery of development to the end of the warranty period, as well as the OutTasking service (technical assistance or task outsourcing).
The internal HelpDesk service provided by this department to its internal clients is excluded.
5. ROLES AND RESPONSIBILITIES OF THE SMS
The document “SGS01 Roles and Responsibilities” and the associated matrix show those responsible for the roles established by the SGS, as well as the person or persons of the company to whom, in situations of leave, illness or temporary absence of those responsible, the tasks corresponding to their role are delegated.
6. SERVICE IMPROVEMENT PLAN
There is a Service Improvement Plan document detailing the annual objectives of the Service Management System, without prejudice to the fact that each SMS process has defined its own particular annual objectives.
The objectives of the Service Improvement Plan are established annually and are reviewed on a quarterly basis.